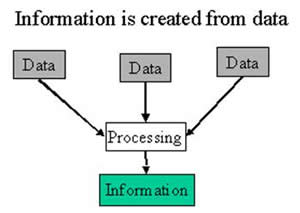
Data are collection of numbers, alphabets or some facts which are unorganized, but able to be organized into useful information.
Information, on the other hand, gives meaningful facts to the user by using the data. Information is obtained by processing the raw data.
Data processing is the process of converting the data into information. The computer processes data to give meaningful information by following set of instructions given by the user.
There is no hard and fast rule for determining when data becomes information. A set of letters and numbers may be meaningful to one person, but may have no meaning to another. Information is identified and defined by its users.
For example, when you purchase something in a departmental store or shopping mall, a number of data items are put together, such as your name, address, products or items you bought, the number of items purchased, the price, the tax and the amount you paid. Separately, these are all data items but if you put these items together, they represent information about a business transaction.
Data Processing Functions:
Electronic Data Processing Modes:
Computers are programmed to process data in different ways. Examples of processing modes are:
1. Online Processing
2. Real-Time processing
3. Distributed Processing
4. Time-Sharing
5. Batch Processing
6. Multitasking
7. Interactive Processing
Online Processing
In this processing mode, data is processed immediately it is received.
Example: When booking a seat on an airline, the seat is booked immediately. This is to avoid problems of double-booking. other example of online processing is when playing computer games online
Real-Time Processing
In real time processing the computer processes the incoming data as soon as it occurs, up-dates the transaction file and gives an immediate response that would affect the events as they happen.
There is no much difference with online processing however with real-time processing, the outcome of the processing is required immediately to influence decision making and not necessarily through online means but can be within a machine.
Example: in nuclear power stations, a certain level of temperature is required to be maintained for effective disintegration of atoms. If the temperatures are not controlled, the system may cause an emergency situation- like in increase or decrease in slight temperature fluctuations, therefore computers are used to control the air conditioning systems at the plant because they are programmed to provide instant answers upon a slight change in temperature has occurred- that is what we call real-time processing
Another example: is the use of humidifiers and dehumidifiers in the computer lab, when there is a lot of humidity, computers turn on the dehumidifiers and vice versa
Distributed data processing
These points to dividing (distributing) processing tasks to two or more computers that are located on physically separate sites but connected by data transmission media; there may be a central computer that receives input from the remote computers (terminals), processes the data and updates the master file. If required, the output can be communicated back to the remote terminals.
Example: When you withdraw money from a bank, your records are transacted and updated in the main server computer which will also update client computers across the bank branches divide.
Batch Processing
In batch processing, data is accumulated as a group (batch) over a specified period of time e.g. daily, weekly or monthly.
The batch is processed at once. E.g. in a payroll processing system, employees details concerning number of hours worked, rate of pay, and other details are collected for a period of time, say one month. These details are then used to process the payment for the duration worked.
other areas where batch processing can be applied include:
Information, on the other hand, gives meaningful facts to the user by using the data. Information is obtained by processing the raw data.
Data processing is the process of converting the data into information. The computer processes data to give meaningful information by following set of instructions given by the user.

There is no hard and fast rule for determining when data becomes information. A set of letters and numbers may be meaningful to one person, but may have no meaning to another. Information is identified and defined by its users.
For example, when you purchase something in a departmental store or shopping mall, a number of data items are put together, such as your name, address, products or items you bought, the number of items purchased, the price, the tax and the amount you paid. Separately, these are all data items but if you put these items together, they represent information about a business transaction.
Data Processing Functions:
Data processing may involve various processes, including:
- Validation – Ensuring that supplied data is correct and relevant.
- Sorting – "arranging items in some sequence and/or in different sets."
- Summarization – reducing detailed data to its main points.
- Aggregation – combining multiple pieces of data.
- Analysis – the "collection, organization, analysis, interpretation and presentation of data."
- Reporting – list detail or summary data or computed information.
- Classification – separation of data into various categories.
Electronic Data Processing Modes:
Computers are programmed to process data in different ways. Examples of processing modes are:
1. Online Processing
2. Real-Time processing
3. Distributed Processing
4. Time-Sharing
5. Batch Processing
6. Multitasking
7. Interactive Processing
Online Processing
In this processing mode, data is processed immediately it is received.
Example: When booking a seat on an airline, the seat is booked immediately. This is to avoid problems of double-booking. other example of online processing is when playing computer games online
Real-Time Processing
In real time processing the computer processes the incoming data as soon as it occurs, up-dates the transaction file and gives an immediate response that would affect the events as they happen.
There is no much difference with online processing however with real-time processing, the outcome of the processing is required immediately to influence decision making and not necessarily through online means but can be within a machine.
Example: in nuclear power stations, a certain level of temperature is required to be maintained for effective disintegration of atoms. If the temperatures are not controlled, the system may cause an emergency situation- like in increase or decrease in slight temperature fluctuations, therefore computers are used to control the air conditioning systems at the plant because they are programmed to provide instant answers upon a slight change in temperature has occurred- that is what we call real-time processing
Another example: is the use of humidifiers and dehumidifiers in the computer lab, when there is a lot of humidity, computers turn on the dehumidifiers and vice versa
Distributed data processing
These points to dividing (distributing) processing tasks to two or more computers that are located on physically separate sites but connected by data transmission media; there may be a central computer that receives input from the remote computers (terminals), processes the data and updates the master file. If required, the output can be communicated back to the remote terminals.
Example: When you withdraw money from a bank, your records are transacted and updated in the main server computer which will also update client computers across the bank branches divide.
Time-Sharing
Just as the name suggests, time-sharing refers to many terminals connected to a central computer and given access to the central processing unit apparently at the same time this sounds like ‘round robin’. Each user is allocated a time slice of the CPU in sequence.
The amount of time allocated to each user is controlled by a multi-user operating system. If a user’s task is not completed during the allocated time slice, he/she is allocated another time slice later in a round robin manner.
Just as the name suggests, time-sharing refers to many terminals connected to a central computer and given access to the central processing unit apparently at the same time this sounds like ‘round robin’. Each user is allocated a time slice of the CPU in sequence.
The amount of time allocated to each user is controlled by a multi-user operating system. If a user’s task is not completed during the allocated time slice, he/she is allocated another time slice later in a round robin manner.
Batch Processing
In batch processing, data is accumulated as a group (batch) over a specified period of time e.g. daily, weekly or monthly.
The batch is processed at once. E.g. in a payroll processing system, employees details concerning number of hours worked, rate of pay, and other details are collected for a period of time, say one month. These details are then used to process the payment for the duration worked.
other areas where batch processing can be applied include:
- Processing bank cheques
- Printing of bank statements
- Updating of a stock database
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing refers to the processing of more than one task apparently at the same time. This is possible in computers like mainframes and network servers.
A computer may contain more than one independent central processing unit which works together in a coordinated way. At a given time, the processors may execute instructions from two or more programs or from different parts of one program simultaneously.
Multiprocessing refers to the processing of more than one task apparently at the same time. This is possible in computers like mainframes and network servers.
A computer may contain more than one independent central processing unit which works together in a coordinated way. At a given time, the processors may execute instructions from two or more programs or from different parts of one program simultaneously.
Multi-programming
Also referred to as multitasking- refers to a type of processing where more than one program are processed apparently at the same time by a single central processing unit.
Unlike multiprocessing, in multitasking, the computer has only one CPU. The computer allocates each program a time slice and decides what order they will be executed.
Also referred to as multitasking- refers to a type of processing where more than one program are processed apparently at the same time by a single central processing unit.
Unlike multiprocessing, in multitasking, the computer has only one CPU. The computer allocates each program a time slice and decides what order they will be executed.
Interactive Processing
There is a continuous dialogue between the user and the computer.
As the program executes, it keeps on prompting the use to provide input or respond to prompts displayed on the screen.
There is a continuous dialogue between the user and the computer.
As the program executes, it keeps on prompting the use to provide input or respond to prompts displayed on the screen.



